Continuous Raster Data Examples
Raster data is a representation of images in rows and columns of pixel format and it is a continuous data representation. The plots in this section use the surface of a 2d density estimate of the faithful dataset 36 which records the waiting time between eruptions and during each eruption for the Old Faithful geyser in Yellowstone Park.
Discrete And Continuous Data Arcmap Documentation
And GIS software a general-purpose application program that is intended to be used in many individual geographic.
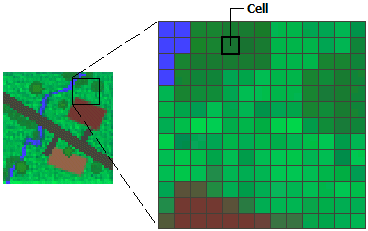
. Color is a major aesthetic element to map to the data points. A feature is anything you can see on the landscape. A grid of cells represents this data.
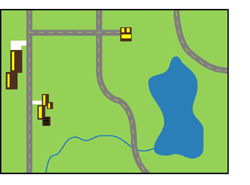
Cloud points can be difficult to interpret due to the sheer number of. Colour gradients are often used to show the height of a 2d surface. Oil depth across an open-water oil spill soil pH reflectance in a certain band in the electromagnetic spectrum elevation landform aspect compass bearing of steepest downward descent salinity of a water body Here is a diagrammatic model of how raster datasets represent real-world features.
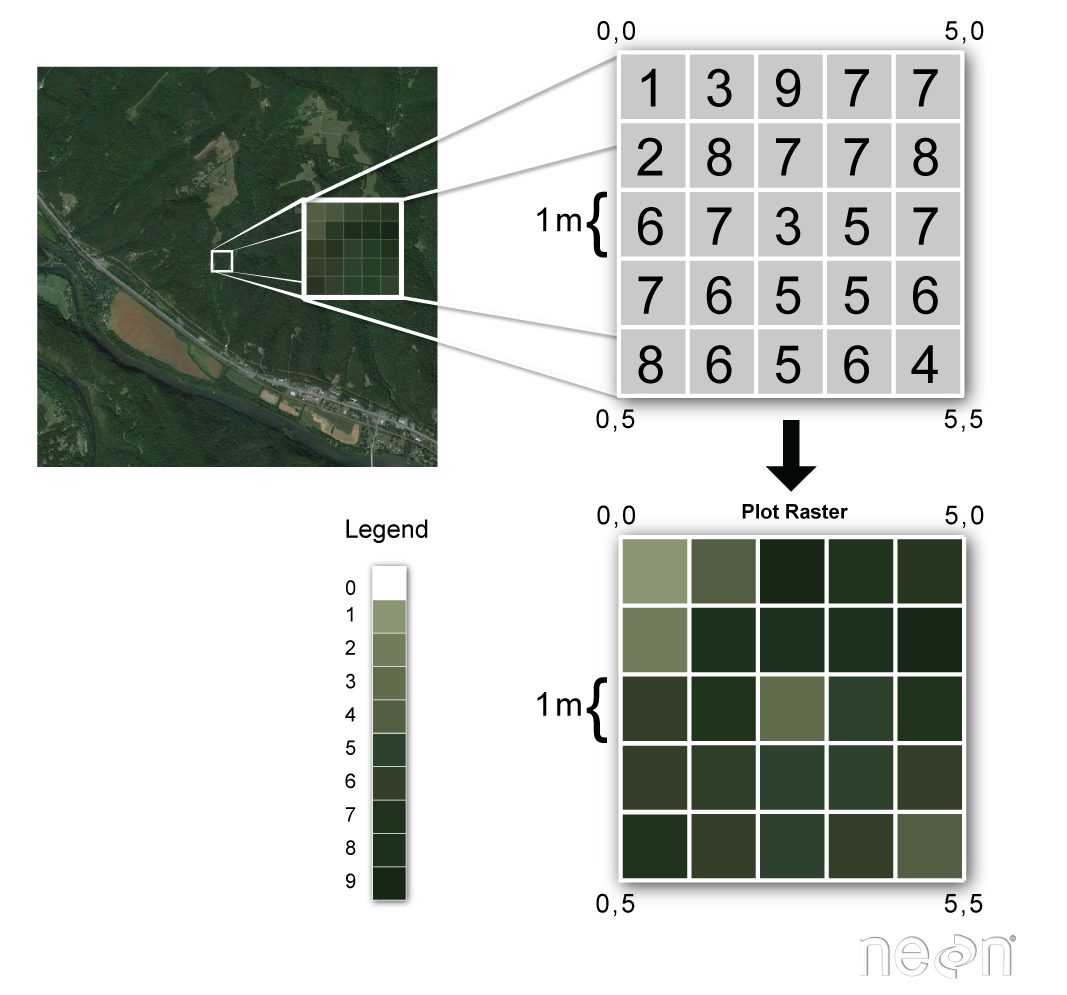
The continuous surface representation of a raster dataset represents some measure such as the height concentration or magnitude for example elevation acidity or noise level. In other words it is a matrix of cells organized into rows and columns. So creating a point density raster from this data would only make sense if we were.
The continuous surface representation of a raster dataset represents some measure such as the height concentration or magnitude for example elevation acidity or noise level. Some examples of continuous data are. Some of the information is also publicly available.
Intro to Point Cloud Layer. Take me to the top of the page. The MOD44B Version 6 Vegetation Continuous Fields VCF yearly product is a global representation of surface vegetation cover as gradations of three ground cover components.
PDAL - Point Data Abstraction Library. Vector Tile Layer from JSON. Satellite imagery databases provide access to affordable satellite images.
Antialiasing is a technique used in computer graphics to remove the aliasing effect. The examples which follow are generally oriented around a NYC taxi pickup dropoff dataset found here. Satellite images photogrammetry and scanned maps are all types of raster-based Earth Observation EO data.
Generally cells are assigned a. ColorRamp2 provides an exact way for mapping continuous values. Vector data is the representation of spatial features in points lines polygon formats and it is a discrete data representation.
The spatial raster data model represents the world with the continuous grid of cells often also called pixels. Variables that may not be continuous probabilities00 may be best viewed via use of raster plots. In computer graphics and digital photography a raster graphic represents a two-dimensional picture as a rectangular matrix or grid of square pixels viewable via a computer display paper or other display mediumA raster is technically characterized by the width and height of the image in pixels and by the number of bits per pixelRaster images are stored in image files with varying.
Each cell has a value that represents information. 112 Continuous colour scales. In the GIS world there are two primary data formats one is a vector and another one is raster data formats.
The distinction must be made between a singular geographic information system which is a single installation of software and data for a particular use along with associated hardware staff and institutions eg the GIS for a particular city government. I hide the legends and set expand to 0 to focus on the appearance. The About page provides high level overview of the library and its philosophy.
Vector data provide a way to represent real world features within the GIS environment. The following code uses functions introduced in a later section. This data model often refers to so-called regular grids in which each cell has the same constant size.
Looking down you can see houses roads trees rivers and so on see figure_landscapeEach one of these things would be a feature when we represent them in a GIS Application. 15 Scales and guides. Because they use specially treated heat-activated paper the printers require no ink toner or.
Each pixel has an associated value. Note that using gsn_csm_contour results in the raster bins at the edges being reduced to half width. Percent tree cover percent non-tree cover and percent non-vegetated bare.
Chemical concentrations and elevation surface are some examples of raster data. But its use in our terminology is an important reminder that the points we are working with are just samples of some continuous field whose spatial variation we are attempting to model. The 57 mm wide thermal print head uses 672 individually addressable dots to form individual raster lines of data at 300 dots per inch across the print headthe 101 mm wide print head uses 1248 dots.
A simple scatter plot does not show how many observations there are for each x y valueAs such scatterplots work best for plotting a continuous x and a continuous y variable and when all x y values are uniqueWarning. Raster data consists of pixels. 14223 Sample Experimental Variogram.
Raster data is. Both use 300 dots per inch in the travel direction as directed by the print control data. Users specify a vector of break values and a vector of colors all the other colors are linearly interpolated between the correspoding break values.
What is Raster Data. The aliasing effect is the appearance of jagged edges or jaggies in a rasterized image an image rendered using pixels. Surface interpolation tools make predictions from sample measurements for all locations in an output raster dataset whether or not a measurement has been taken at the location.
Change point size and density. These clearly show the bin and data resolution. The problem of jagged edges technically occurs due to distortion of the image when scan conversion is done with sampling at a low frequency which is also known as.
Imagine you are standing on the top of a hill. Come back to this after reading section 752 which introduces methods for plotting two. The practical goals of the toolbox mean that topics are introduced when they are most relevant.
Filter points in a Point Cloud Layer. The scales toolbox in Chapters 10 to 12 provides extensive guidance for how to work with scales focusing on solving common data visualisation problems. Dynamic data layer with raster data.
Visit Readers and Writers to list data formats it supports and see Filters for filtering operations that you can. Surface interpolation tools make predictions from sample measurements for all locations in an output raster dataset whether or not a measurement has been taken at the location. Raster data stores information of features in a matrix of cells or pixels organized into rows and columns either discrete or continuous.
In circlize there are two functions that provides customization of colors. PDAL is a C library for translating and manipulating point cloud dataIt is very much like the GDAL library which handles raster and vector data. VCF products provide a continuous quantitative portrayal of land surface cover at 250 meter m pixel.
Commercial satellite data providers sell satellite images data and information or they can be commissioned to provide continuous delivery of data for example from a specific area. For example scale transformations are discussed in relation to continuous position scales Section 1017.

Introduction To Raster Data Introduction To Geospatial Concepts

What Is Raster Data Help Documentation
Introduction To Raster Data Introduction To Geospatial Concepts
Introduction To Raster Data Introduction To Geospatial Concepts
0 Response to "Continuous Raster Data Examples"
Post a Comment